
In 2006 the first Think Coffee store opened near NYU. In this store, founder Jason Scherr wanted to cultivate and amplify “coffee shop energy.” Meaning he wanted to start a coffee shop that attracted people that cared for social issues like the environment and giving back to the community. Scherr’s new Think enterprise had to lead by example, so they introduced composting and a re-usable cup program called HuskeeSwap at their stores. Think also gave back by donating profits to local nonprofits. But soon, that wasn’t enough.
Scherr and his team began becoming more interested in where their product comes from, what the supply chain looks like, and who is most vulnerable in that space. In 2012, Think wanted to go beyond their existing waste reduction practices and local giving.
Meet Enrique Hernandez, COO of Think Coffee
Hernandez came on board in 2014 and soon after became the boots on the ground in all the countries Think sourced their coffee from. He spoke with growers, suppliers, but most importantly, the farmworkers. Hernandez and his team quickly understood that the Fair Trade coffee they’d been paying a premium for might not be as fair as they thought.
Is Fair Trade Really Fair?
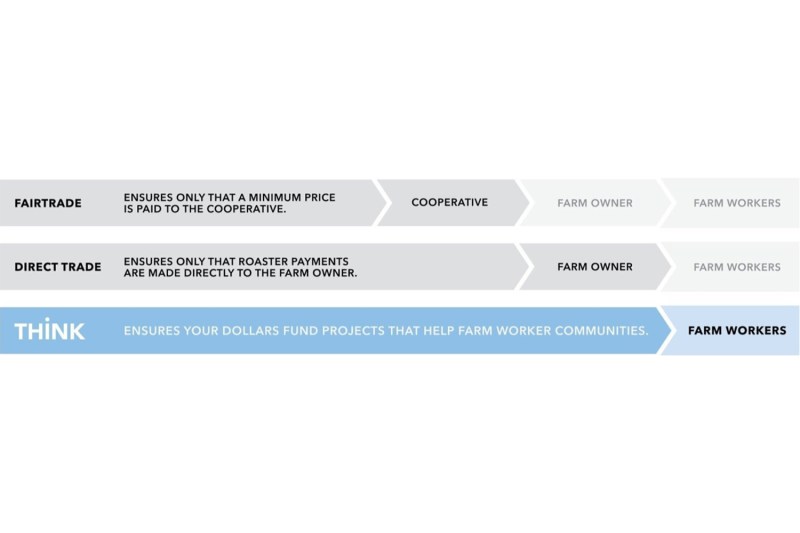
Think began to question how their coffee gets to their customers and obtains its Fair Trade and Direct Trade coffee certifications. This is where they found holes in the system. Before we go on, it’s important to understand the Fair Trade and Direct Trade models.
Coffee is a commodity. Not unlike a currency, its price is determined by the market. With commodities, the country that produces the most product for export controls the price. Brazil has more coffee than any other country globally (around 3M tons), so they can set the price. Which in turn means a fortune for coffee farm owners and big-name wholesalers, but not so much for the farmworkers in developing countries where coffee grows. The Fair Trade model was developed to ensure that farmworkers in these countries earned a decent wage, and this is why we pay more for Fair Trade coffee.
Although the concept is noble, Think found that it isn’t the most transparent or effective way to meet the needs of the farmworkers at origin. There’s no guarantee that farmworkers ever see a dime of the added dollars we pay for Fair Trade coffee. Also, a fair trade certification comes with a hefty fee that farm owners must pay, which small farm owners in impoverished countries simply can’t afford. In the Direct Trade model, deals are struck between growers and buyers to pay more for quality beans. Still, there’s nothing ensuring workers see any bump in pay.
“A large Fair Trade coffee exporter sources coffee from many farms, some large and some small. There’s a tendency for exporters to only list their larger farms, and the small farms lose out when the Fair Trade Commission performs its audits.”
The Think Business Model
“We realized we need to do more…we have a bigger responsibility,” Hernandez said. This statement goes beyond just providing a decent wage to farmworkers. Think began to step into their lives and ask, “How can we help?” The answers were different for different regions, but the workers responded with things like clean water, housing, and menstrual supplies for women and young girls.
To provide this help, Think knew that to truly help people at the coffee’s origin, it would have to pay even more than the Fair Trade premium for its product. To charge this premium, the company had to be extremely transparent and get its coffee direct from the source.
So that’s what the Think Coffee team did. It made deals with growers and producers in four different countries and paid at least 50% over the current Fair Trade minimum as published by the Fair Trade Labeling Organization (FLO). This premium factors in both higher wages for the workers and the social projects for the region. By forming this model and attributing an extra premium for a specific project in a region, Think believes it will be easier for more coffee companies to understand and accept.
However, the business model doesn’t end there. Think also knew that its customers would be paying for a large chunk of this premium, so it had to be fully transparent. That’s why all of the coffee costs and inventory data are made public on its website. That way, if the customer wants to do the math on their premium, they can see exactly how much they contribute to each social project.
How Think is Giving Back

In 2012 Think started to visit the sources of their coffee and began to understand their needs, Nicaragua being the first. Santa Isabel, Nicaragua, said they needed clean water access. Santa Teresa, Nicaragua, needed worker housing. So, after securing funding, Think and the team have given over 653 people clean water access and helped restore 76 worker homes over time.
As the Think footprint began to grow, they sought out more single-origin coffee from different countries. Expanding into other countries came with different worker needs and new challenges on how to provide for them. In Ethiopia, Hernandez learned there was a huge need for menstrual supplies for women and young girls. Hernandez and the team teamed up with women in the community to provide 1,500 (and counting) menstrual kits.
“Every month when it’s a girl’s cycle, they stay home from school. Then they fall behind, and many drop out. We wanted to combat that.”
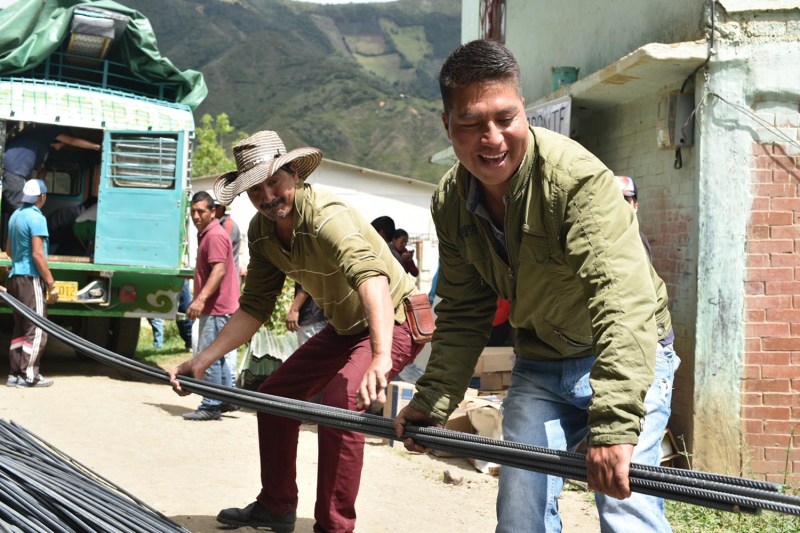
In Columbia, the need was once again housing for the coffee farmworkers whose homes were devastated by earthquakes. Since 2016 over 100 tons of building materials have been delivered so that 74 homes could be rebuilt.
How You Can Support

These contributions may seem small compared to the massive amount of need in the developing countries where our coffee comes from. But in reality, the impact on the workers’ lives is enormous. If more coffee companies partnered with Think and adapted their model, the effect could be massive. Not just massive, it could change the entire world of coffee.
The problem is, change is hard. Big-name coffee companies need to want to put people before profits. Consumers must be willing to pay significantly more for their cup of joe. However, the hope is, if the industry could adapt to Think’s transparent business model, most (if not everyone) would be on board.
If you own a coffee shop, consider partnering with Think. If you work in the coffee industry, raise awareness of the Think Coffee business model by mentioning it to your boss. Or, if you’re a coffee drinker (like most of us), you can buy and subscribe to Think online. You can view the impact of every bag of coffee you purchase.
This feature is part of our Brands Giving Back Series, where we’ll bring you all the latest news on brands that are giving back to the community, and how you can support them by shopping online.



