If this summer has got you feeling like an ant under the magnifying glass, welcome to the club. More Americans than ever are expected to suffer through extreme temperatures over the next 30 years, according to a national risk assessment released by the First Street Foundation. Extreme heat waves, in fact, are expected to last longer and impact more communities as the climate continues to warm. By 2050, the nonprofit assessing climate change risk predicts an “extreme heat belt” to wrap around the southeastern and western United States, affecting over 107 million residents.
What does First Street define as ‘extreme’? How about over 1,000 U.S. counties projected to experience at least one day above 125 degrees by 2053. Yikes. This real estate over this extreme heat belt rolls down the West Coast into northern Texas, Louisiana, and Florida. The dark red blotches aren’t isolated to southern climes, though, stretching as far north as Illinois, Indiana, and even Wisconsin.
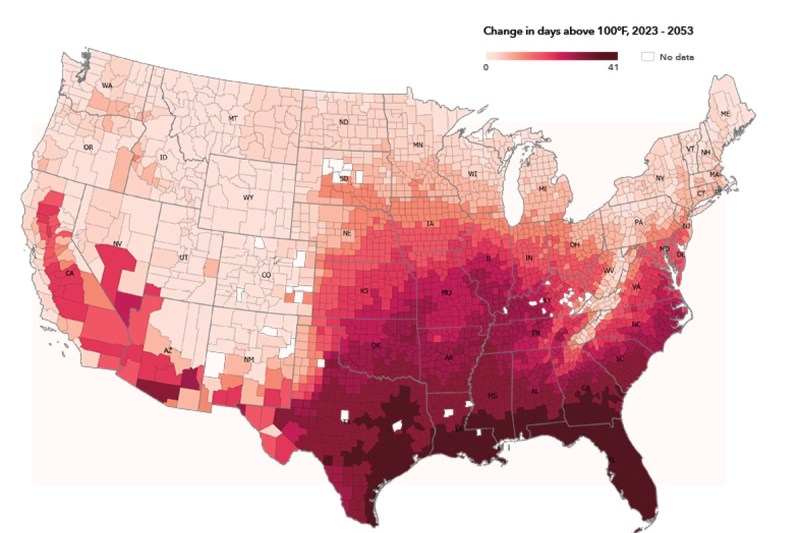
The peer-reviewed extreme heat model is the research and technology nonprofit’s sixth National Risk Assessment of hazardous heat. The model measures the seven hottest days expected for any property this year, and extends that metric to estimate how many of those days could be experienced in the next three decades.
First Street identifies these potentially hazardous climates so that homeowners can prepare for increasingly inclement conditions. The report assesses “how the frequency, duration, and intensity of extremely hot days will change over the next 30 years,” illustrating how changing climate conditions impact personal property. This analysis arises from “high-resolution measurements of land surface temperatures, canopy cover, impervious surfaces, land cover, and proximity to water to calculate the current heat exposure, and then adjusts for future forecasted emissions scenarios”.
For 2023, the model found 50 counties that are home to 8.1 million residents expected to experience temperatures above 125 degrees in 2023 — the highest level in the National Weather Services’ heat index. By 2053, 1,023 counties are expected to exceed this temperature, an area that is home to 107.6 million Americans and covers a quarter of the U.S. land area.

“We need to be prepared for the inevitable, that a quarter of the country will soon fall inside the Extreme Heat Belt with temperatures exceeding 125°F and the results will be dire,” Matthew Eby, founder and CEO of First Street Foundation, said in a press release.
NWS data reveals extreme heat to be, by far, the top weather-related killer in the U.S. How do you die when it’s hot? Heat-related illness occurs when the body can no longer cool itself due to insufficient levels of fluid and/or salt after sweating too much and not consuming enough water dehydration. A combination of high heat and humidity can lead to muscle cramps, heat exhaustion, and finally heat stroke.
The most at risk are often the people with the least means to adapt to the situation: kids, the elderly, people of color, and poor folk. According to the NWS, this risk is multiplied in dense urban centers that create urban heat islands. Construction can also magnify these conditions.
The Washington Post found that, by the middle of this century, “71 percent of the poorest neighborhoods in the country will likely endure severe heat.”
Extreme heat will also make outdoor work more dangerous. First Street estimates that there are roughly 3.8 million outdoors workers today who experience at least one annual severe heat wave. In 30 years, the model estimates that number to jump nearly 30 percent to 4.9 million people.
The most severe shift in local temperatures, for example, is in Miami-Dade County where the model posits that its seven hottest days, currently at 103 degrees, will increase to 34 days at that same temperature by 2053.

First Street’s prognosticator is now incorporated with its Risk Factor tool, for every property in the contiguous United States. Risk Factor users can not only determine their Heat Factor in the next 30 years, but assess their Flood Factor and Fire Factor as well, learning the specific risks to their location.
These extremes could suggest a lot more climate migration and a very different real estate market very soon.
“If people move then you have an impact to the tax base and changes to demand for properties and values overall,” Eby told CNBC.



